Histogram Examples
Take a look at some histogram examples showing actual images and their corresponding histograms. This will help you in understanding histograms, the relationship between image characteristics, and the shape of the associated histogram.
If you can’t yet answer What is a Histogram?, and would like more background on how to interpret a digital photography histogram, then read these sections first.
Images and their Corresponding Histograms
The first image is a close-up of a white carnation. It contains mostly light tones. This is reflected in the image histogram, which has a large "hump" to the right of the graph, and very little data on the left.

An image containing mostly light tones.
©Julie Waterhouse Photography
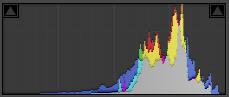
Corresponding histogram
For the second of the digital photography histogram examples, I have an image of a pink daisy. It has an almost-black background, and a medium-toned flower. Its image histogram shows a large spike near the left, which represents the background, and then a hump near the middle that represents the flower.

An image containing a dark-toned background,
and mid-toned subject.
©Julie Waterhouse Photography
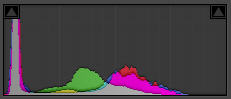
Corresponding histogram
For the third of the digital photography histogram examples, I have an image of a pair of gerberas. It has a light background this time, with the same mid-tone flowers. In this case, the image histogram has a spike near the right representing the background, and a low hump in the middle representing the flowers.

An image containing a light-toned background
and mid-toned subject.
©Julie Waterhouse Photography
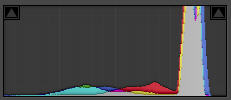
Corresponding histogram
For the fourth of the digital photography histogram examples, the image is a landscape at sunrise. The sky is extremely bright, and the foreground is very dark. This is a situation in which the dynamic range of the scene exceeds the camera’s capabilities, and we see clipping on both the left and right sides of the corresponding image histogram. We have lost detail in both the shadows and the highlights.

Landscape with high dynamic range.
©Julie Waterhouse Photography
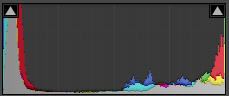
Corresponding histogram with clipping
in both the whites and blacks.
For the fifth and final of the digital photography histogram examples, the image is a very low-contrast landscape. Here, our histogram does not approach the right or left, since there are no whites or blacks in the image. The image histogram shows a large hump in the mid-tones, and nothing in the shadows or highlights.

Low-contrast landscape
©Julie Waterhouse Photography
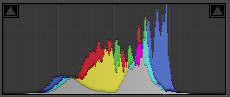
Corresponding histogram
The final image is a result of processing the previous one in a camera RAW editor to increase the contrast. Exposure was increased by +1.36 stops, and the black point was also adjusted up. Now the image histogram shows a full range of contrast from light to dark, but without clipping. As you can see from the histogram, the largest number of pixels are found in the light tones, which corresponds to the light blue sky.

Contrast increased.
©Julie Waterhouse Photography
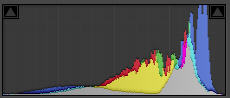
Corresponding histogram.
For more information on this topic, check out my photo histogram video tips.
Or, you may be interested in learning about resizing photos.